Bipolar 1 ICD 10: Everything You Need to Know: In order to bill for bipolar disorder, a mental health illness characterized by extreme psychological highs and lows, healthcare practitioners utilize the ICD 10 code for bipolar disorder.

Millions of people around the world suffer from the complicated illness of bipolar disorder, highlighting the need for healthcare professionals to properly identify and document it. This essay examines the field of bipolar illness and the value of ICD 10 codes in comprehending and treating this disorder.
An Overview of The Symptoms and Manifestations of Bipolar
The psychiatric illness known as bipolar disorder, formerly known as manic-depressive illness, is marked by extreme mood shifts between manic and depressive episodes.
People may have higher energy levels, greater impulsivity, and a greater sense of exhilaration during manic episodes. In contrast, depressive episodes are characterized by extreme lethargy, profound sorrow, and a general feeling of hopelessness.
These mood swings might interfere with several facets of a person’s life. People experiencing manic phases may have poor judgment and engage in hazardous behaviors, whereas depressive episodes might make it difficult to complete everyday chores, resulting in social isolation and a decrease in enjoyment of previously enjoyable activities.
The fluctuation between these situations puts a strain on interpersonal relationships within the family and community as well as on the person. Because mood swings are unpredictable, it can be difficult for friends and family to comprehend and deal with the changes in behavior. Variations in energy levels and attention can also impede academic and professional opportunities.
What Is the ICD-10 Code for Bipolar Disorder?
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Edition (ICD-10), is a widely used coding system that classifies various health conditions, making it easier for healthcare professionals to communicate and diagnose patients accurately. This approach is quite effective in promoting consistency in medical bills and documentation.
ICD 10 Code for Bipolar Illness: F31
The ICD code for bipolar illness, F31, is included in the large ICD-10 list. This alphanumeric code acts as a unique identifier for insurance companies, healthcare providers, and researchers. The use of ICD-10 codes improves the accuracy of medical records and guarantees that bipolar disorder is recorded in a consistent manner.
Distinctions Between the ICD 10 Codes for Bipolar I and Bipolar II?
Bipolar I Disorder (F31.0)
The defining feature of Bipolar I Disorder is the presence of at least one manic episode, which may be accompanied by hypomanic or major depressive episodes. Knowing the exact ICD 10 code (F31.0) for bipolar I disorder helps to differentiate it from other variations.
(F31.81) Bipolar II Disorder
The bipolar disorder ICD 10 code (F31.81) for Bipolar II makes it easier to distinguish and recognize it inside the coding system. Recurring depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes characterize Bipolar II Disorder, but not complete manic episodes. It’s important to distinguish between Bipolar 1 and Bipolar II because the therapy for each can be very different.
Additional ICD 10 Codes for Bipolar Disorder Subtypes and Specifiers
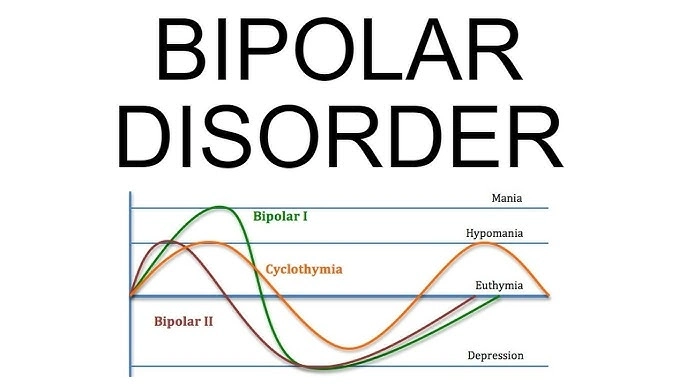
Cyclothymia (F34.0)
Cyclothymic Disorder is a less severe version of bipolar disorder that is marked by frequent episodes of hypomanic and depressive symptoms. The Cyclothymic Disorder subtype is adequately documented because of its ICD 10 code for bipolar disorder (F34.0).
In order for healthcare providers to properly record the subtle manifestations of bipolar illness, it is essential for them to understand these subtypes and their associated ICD 10 codes.
Therapeutic Strategies Based on Data
Integrating these evidence-based therapeutic methods into the therapy plan provides a comprehensive and individualized approach to treating bipolar disorder, addressing the underlying causes of the disorder’s complexity as well as the symptoms.
Behavioral and Cognitive Therapy (CBT)
For those suffering from bipolar disorder, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has proven to be a potential therapeutic strategy. The goal of this psychotherapy intervention is to recognize and change maladaptive behaviors and thinking patterns. CBT helps people identify triggers and early warning signs of mood episodes when they have bipolar disorder.
Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT)
A particular kind of psychotherapy called Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT) focuses on the connection between interpersonal relationships and the management of daily routines. Disruptions in sleep-wake patterns and social rhythms can cause mood episodes in people with bipolar disorder.
Therapy that prioritizes families (FFT)
Family-Focused Therapy (FFT) is a vital component of a holistic approach to treatment because it acknowledges the effects of bipolar disorder on family relationships. This strategy includes teaching family members about the characteristics of bipolar disorder, improving communication abilities, and creating a supportive atmosphere.
Drugs
The foundation of bipolar disorder treatment is pharmacotherapy. Mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants are frequently used to help control mood fluctuations. Lithium, specifically, is a popular mood stabilizer that has been proven to be effective in preventing both manic and depressive episodes. The prescription is chosen according to each patient’s unique needs and reaction. Regular monitoring and adjustment of medication, under the supervision of a psychiatrist, are crucial aspects of the treatment plan.
Psychoeducation
In order for people with bipolar illness to take an active role in their therapy, psychoeducation is essential. By fostering a sense of control and self-efficacy, psychoeducation contributes to the overall management and well-being of people living with bipolar disorder. This educational strategy offers thorough details on the nature of the illness, its possible triggers, and successful coping mechanisms. In addition to improving the person’s knowledge of their condition, psychoeducation also encourages compliance with treatment regimens.
Summary
The ICD-10 code for bipolar illness is F31, with particular codes like F31.0 for Bipolar I and F31.81 for Bipolar II to distinguish between subtypes for correct diagnosis and billing. Providers can improve their skills by signing up for an insurance billing course for therapists.
For people with bipolar disorder, evidence-based therapies like CBT, IPSRT, Family-Focused Therapy, and medication are essential for mood stabilization and quality of life improvement.
Correct coding and documentation are essential for maintaining continuity of care and adherence to insurance and reimbursement regulations.
Using integrated billing and EHR software such as TheraPlatform can automate duties such as claims submission, invoicing, and payment tracking, which saves providers time and reduces errors.






